Sounds That May Have Killed
It is well established that low frequency sound can have a notable impact on humans, animals, and may be deleterious to health.[1] Just like the abundance of frequencies contained in a vocal sample, environmental sounds have oscillations that can be evaluated for health influences on individuals exposed to such resonances. Recently it was reported from many geographic locations that a “low rumbling” mysterious sound could be felt and heard. Reportedly, the sounds were causing people to feel mentally disoriented and even physically ill.
Diplomats and their families from China, Cuba, Canada and the US have reported an unusual collection of symptoms that range from dizziness, nausea, concussions, hearing loss, disorientation and unexplained fatigue. 2
As reported by CNN, Dr. Jeffrey Kim of Georgetown University’s Otolaryngology Department states that “It is possible to create a complex sound of certain frequencies and acoustic patterns that could affect our body function especially brain function.”
For these reasons, the Institute of BioAcoustic Biology in Albany, Ohio, USA, (the leading experts in the field of the effects of sound on living systems), has evaluated the frequencies being reported as detrimental and may have determined why many political opponents, whistleblowers and pharmaceutical enemies have been found dead in their homes or hotels from unexplained heart attacks.
The main constituents of the recently documented sounds are frequencies that have been identified as being associated with stroke, heart attacks, cellular oxygen and cellular communication. Below is a short list of the major bio-frequencies found in the ambient sound sample. Items marked in green are associated with heart and circulatory issues.
Think of the brain as a Central Process Unit, like a computer’s CPU hard drive. The brain is dominated by frequencies that are sent along neuro pathways to direct, manage, and communicate with the body. It has been absolutely the case that disturbances in these pathways have a direct influence on body function and psychological states of being. An example of this is found in the Gate Control Theory of Pain.2
Below additionally is a more comprehensive listing of the health base bio-frequencies correlates that are associated with feelings of malaise.
Arsenic is often used as a foundation for blood thinner; including rat poison.
Significant Correlates
| NAME | REL | PAIRS | TAG | CATEGORY | USE |
| Thrombomodulin | 13 | Low | Protein | Anti-coagulant activities | |
| C-Reactive Protein | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Associated inflammation |
| Thrombomodulin | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Anti-coagulant activities |
| Thromboxane A synthase 1 | 17 | 0.06 | Low | Epigenetic | Assoc. w/ cancer, stroke, platelet aggregation |
| Synapsin 1 | 28 | High | Epigenetic | involved w/ neurotransmitter release | |
| Prostaglandin E2 | 28 | High | Biochemical | levels maybe elevated due to depression |
| Acetaldehyde | 28 | High | Toxin | may cause apathy | |
| Adrenaline | 31 | Lowest Low | Hormone | Dilates blood vessels that supply the brain | |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 31 | Lowest Low | Biochemical | memory transmitters | |
| Aconitase Mitochondrial | 23 | Low | Epigenetic | Protects mitochondrial, genome met. of energy path. | |
| Lipoic Acid | 23 | Low | Vitamin | May help to protect the body from Arsenic Poisoning | |
| Folic Acid | 13 | High | Vitamin | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic | |
| Cholinergic receptor muscarinic 2 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Influences many effects of CNS E peripheral NS |
| Cholinergic receptor muscarinic 2 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Influences many effects of CNS E peripheral NS |
| Acetylcholine CHMR 5 (muscarine) | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Involved w/ personality traits |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ clotting, stroke |
| Fibrinogen alpha gene | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | controls blood clotting assoc. w/ stress |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Protein metabolism, protein binding |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ clotting, stroke |
| Fibrinogen alpha gene | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | controls blood clotting assoc. w/ stress |
| Acetylcholine CHRNA5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Cell comm., signal trans., dev. of nervous system |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic alpha polypeptide 5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Assoc. w/ brain, nervous system dev. |
| Nitric Oxide | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Biochemical | assoc with cellular oxygen |
| Cystine | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Assoc. w/ ADHD, brain, nervous system |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 20 | 0.04 | High | Protein | Assoc. w/ ADHD, brain, nervous system |
| Cystine | 20 | 0.04 | High | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic |
| GABA receptor alpha 5 | 20 | 0.04 | High | Epigenetic | Autism, Praeder Will/Angelman syndrome, bipolar |
| GTP Atlastin | 24 | Low | Epigenetic | ER/Golgi activity, cell comm., signal transduction | |
| Atlastin | 24 | Low | Epigenetic | ER/ golgi activity, spastic paraplegia, brain | |
| Acetylcholine CHRNA 10 (Nicotinic agonist) | 24 | Low | Genome | Transport chain, int. ear, hair cells, skin cells keratinocytes | |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic alpha polypeptide 10 | 24 | Low | Genome | Internal ear, hair cells, pituitary gland, keratinocyte | |
| Solute carrier family 6 member 3 | 24 | Low | Genome | Brain & retina, protect against nicotine dependence | |
| GABA A receptor assoc protein | 16 | High | Protein | Mediates with cytosleleton | |
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic | |
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | Autistics may be deficient in | |
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | Concentrates in brain | |
| NGFR associated protein 1 | 21 | Low | Genome | Oligodendrocytes myelinating cells of CNS | |
| Nerve growth factor NGFR AP 1 | 21 | Low | Genome | Signal transduction, apoptosis | |
| Yellow = Highest Prioirty, Blue = Secondary and Pink, tertiary | Rel – Relevance = the higher the relevance the more significant the issue | ||||
BioAcoustic Opinion
Sound weapons, covert in nature, in addition to loud and boisterous applications, have been with us for decades. This amalgamation of frequencies would very much look like a heart arrhythmia or stroke making this a clever, sinister and almost undetectable method of murdering one’s opponents.
Just a Few Considerations
These examples of recent “heart attacks” in otherwise healthy and even young people raises the issue of whether environmental frequencies, as may be produced by HVAC equipment, or perhaps more from a more sinister source, can lead to not just discomfort, but also death.
- John Heart, the Home Alone movie star found dead in a Palo Alto, Calif., hotel room last month, died of “natural causes” — a heart attack, the Santa Clara County Medical Examiner-Coroner’s Office said Tuesday.[1]
- Sex worker dies from suspected heart attack in hotel room – The body of a commercial sex worker was found on the bed of a city hotel yesterday morning, hours after she checked in with a male companion. The woman, whose name has been given only as “Medusi,” was discovered dead around 09:00 hrs at John’s Beer Garden when police broke into a room she was occupying after she had failed to respond to hotel workers who went to inform her that her allotted time had expired.[2]
- Vadodara : The 33-year-old Russian citizen, who was found dead at a hotel in the city late on Sunday night, died due to heart attack. Russian man found dead in hotel suffered heart attack – Investigating officials said on Monday that the initial postmortem report suggested that the man Alexander Katmonov died of cardiac arrest.[3]
- “He was a heavy smoker and wasn’t in the best health. He had recently been hospitalized for health reasons. Right now we are thinking he probably had a heart attack, but we aren’t ruling anything out …” [4]
[1] https://www.usatoday.com/story/life/2017/08/15/coroner–reports–john–heard–died–heart–attack/570523001/
[2] https://www.kaieteurnewsonline.com/2017/04/18/sex–worker–dies–from–suspected–heart–attack–in–hotel–room/
[3] https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/vadodara/Russian–man–found–dead–in–hotel–suffered–heart–attack/articleshow/54792142.cms
[4] http://www.itemonline.com/news/local_news/huntsville–man–found–dead–in–hotel/article_037ffcb0–1f3d–517a–be6d–b211e67aa017.html
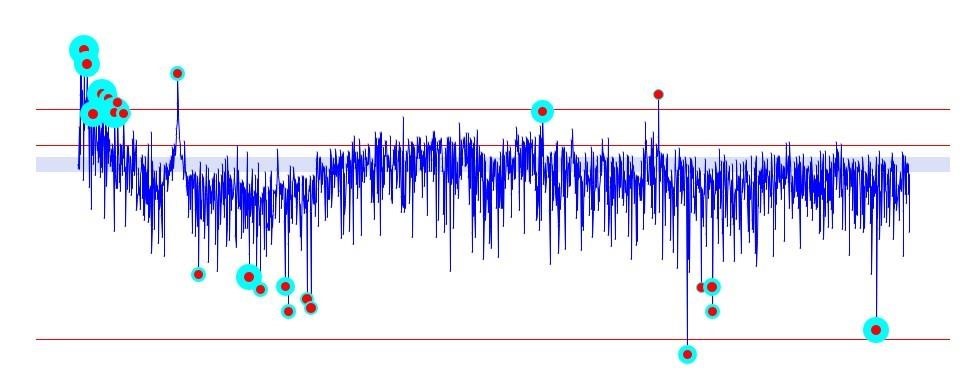
Here is some background information from Wikipedia regarding the substances related to the frequencies analyzed.
Most occurring by pairs –
Thrombomodulin –Thrombomodulin functions as a cofactor in the thrombin-induced activation of protein in the anticoagulant pathway by forming a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. This raises the speed of protein C activation thousand-fold. Thrombomodulin-bound thrombin has procoagulant effect at the same time by inhibiting fibrinolysis by cleaving thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI, aka carboxypeptidase B2) into its active form.
Atropine – Atropine is a medication to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopic. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour.[2] Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings.
Common side effects include a dry mouth, large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate.[3] It should generally not be used in people with angle closure glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during
pregnancy causes birth defects, it has not been well studied. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibiting the parasympathetic nervous system Acetylcholine – acts a neurotransmitter
Arsenic – nutrients to activate blood thinning Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein that in vertebrates circulate in the blood. During tissue and vascular injury it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and subsequently to a fibrin-based blood clot. Fibrinogen functions primarily to occlude blood vessels and thereby stop excessive bleeding. However, fibrinogen’s product, fibrin, binds and reduces the activity of thrombin. This activity, sometimes referred to as antithrombin I serves to limit blood clotting. Loss or reduction in this antithrombin activity due to mutations in fibrinogen genes or hypofibrinogen conditions can lead to excessive blood clotting and thrombosis. Fibrin also mediates blood platelet and endothelial cell spreading, tissue fibroblast proliferation, capillary tube formation, and angiogenesis and thereby functions to promote tissue revascularization, wound healing, and tissue repair.
Reduced and/or dysfunctional fibrinogens occur in various congenital and acquired human fibrinogen related disorders. These disorders represent a clinically important group of rare conditions in which individuals may present with severe episodes of pathological bleeding and thrombosis; these conditions are treated by supplementing blood fibrinogen levels and inhibiting blood clotting, respectively. Certain of these disorders may also be the cause of liver and kidney diseases.
Fibrinogen is a “positive” acute-phase protein, i.e. its blood levels rise in response to systemic inflammation, tissue injury, and certain other events. It is also elevated in various cancers. Elevated levels of fibrinogen in inflammation as well as cancer and other conditions have been suggested to be the cause of thrombosis and vascular injury that accompanies these conditions.
Comprehensive Listing of Correlates:
| NAME | RELEVANCE | PAIRS | TAG | CATEGORY | USE |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 13 | Low | Epigenetic | Huntington’s disease locus | |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 13 | Low | Epigenetic | Assoc. w/ ADHD, brain, nervous system | |
| Thrombomodulin | 13 | Low | Protein | Anti-coagulant activities | |
| C-Reactive Protein | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Associated w/ brain behavior |
| Thrombomodulin | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Anti-coagulant activities |
| FRS3 | 20 | 0.06 | High | Genome | Cell comm., signal transduction, brain only |
| GABA B receptor 1 isoform B | 20 | 0.06 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ MS, epilepsy, schizophrenia |
| RAR related orphan receptor A | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | DNA binding, bone remodeling, neuroprotection |
| Retinoicacid RAR related orphan receptor A | 20 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Neuroprotection, bone remodeling |
| Linoleic acid | 13 | 0.06 | Low | Fatty Acid | Helps prevent degeneration of brain |
| ADP ribosylation factor domain protein 1 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | GTPase activity |
| Nerve growth factor NGFIA binding protein 1 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ metabolism, brain neutrophil |
| P13 kinase pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| GDNF family receptor alpha 4 isoform 1 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Protein | Receptor activity, cell comm., signal trans. |
| Atropine | 17 | 0.06 | High | Med-Analgesic | excessive assoc. w/ anxiety |
| Acetylcholine CHRNB3 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic, beta polypeptide 3 | 17 | 0.06 | High | Epigenetic | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| Germanium | 17 | 0.06 | Low | Mineral | May increase lifespan |
| ADP ribosylation factor domain protein 1 | 17 | 0.06 | Low | Protein | GTPase activity |
| Thromboxane A synthase 1 | 17 | 0.06 | Low | Epigenetic | Assoc. w/ cancer, stroke, platelet aggregation |
| Myelin expression factor 2 | 25 | High | Protein | Assoc. w/ metabolism, trans. regulator activity | |
| Integrin-linked kinase | 25 | High | Epigenetic | Cell comm., transduction, shape, regulate cell cycle | |
| HTR 5- hydroxytryptamine receptor 1e | 25 | High | Epigenetic | Serotonin receptor | |
| Artemin isoform 2 | 25 | High | Genome | Cell comm., signal transduction, growth factor activity | |
| Nerve growth factor early response protein 1 | 25 | High | Protein | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| NGFIA binding protein 2 | 10 | High | Genome | Transcription regulator activity, metabolism | |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic alpha polypeptide 4 | 28 | High | Genome | Nicotine dependence, gen. epilepsy | |
| Acetylcholine CHRNA4 | 28 | High | Genome | Transport chain mod. behavior, nicotine dep., epilepsy | |
| Glycine Solute carrier family 6 member 9 isoform 2 | 28 | High | Epigenetic | Brain, chemical messenger, supraspinal neurotrans. | |
| Vitamin C | 28 | High | Vitamin | may improve condition of manic depression | |
| Vitamin C | 28 | High | Vitamin | excessive stress may deplete | |
| Synapsin 1 | 28 | High | Epigenetic | involved w/ neurotransmitter release | |
| Serotonin | 28 | High | Hormone | insufficient secretion may=aggressiveness | |
| Prostaglandin E2 | 28 | High | Biochemical | levels maybe elevated due to depression | |
| Acetaldehyde | 28 | High | Toxin | may cause apathy | |
| Tyrosine kinase receptor C isoform 2 | 20 | High | Genome | Cell communication, signal transduction | |
| NMDA receptor 2A | 20 | High | Epigenetic | Cell communication, signal transduction | |
| RET isoform 1 | 20 | High | Genome | Persephin neurodegenerative disease | |
| Glucose | 20 | High | Biochemical | Utilized as “fuel” for brain. | |
| Lactic Acid | 20 | High | Biochemical | Excess amounts may cause anxiety | |
| Inositol | 20 | High | Vitamin | Concentrates in brain | |
| Fructose | 20 | High | Biochemical – Sugar | causes depression | |
| Adrenaline | 31 | Lowest Low | Hormone | Dilates blood vessels that supply the brain | |
| Adrenaline | 31 | Lowest Low | Hormone | Neurotransmitter | |
| Pregnenolone | 31 | Lowest Low | Hormone | May be useful for the treatment of phobias | |
| FGF receptor 4 isoform 1 | 31 | Lowest Low | Epigenetic | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 31 | Lowest Low | Biochemical | memory transmitters | |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 31 | Lowest Low | Biochemical | enhances neurotransmission | |
| Diazepam binding inhibitor isoform 1 | 10 | Low | Epigenetic | Pancreatic connections, mitochondrial damage | |
| Tyrosine kinase receptor A isoform 3 | 28 | 0.02 | Low | Protein | Signal transduction, signaling pathway |
| Oncomodulin | 28 | 0.02 | Low | Genome | Regenerates injured nerve fibers, brain, spine |
| Oncomodulin | 24 | 0.02 | Low | Genome | Regenerates injured nerve fibers, brain, spine |
| P13 kinase pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 | 28 | 0.02 | Low | Protein | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| P13 kinase pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 | 24 | 0.02 | Low | Protein | Cell communication, signal transduction |
| Glycl tRNA synthetase isoform 1 | 8 | High | Protein | Assoc. w/ brain, neuronopathy | |
| Aconitase Mitochondrial | 23 | Low | Epigenetic | Protects mitochondrial, genome met. of energy path. | |
| GABA | 23 | Low | Amino Acid | Prevents stress msgs f/ reaching brain – Neurotransmitter | |
| Lipoic acid | 23 | Low | Fatty Acid – derivative | May possess life extension capabilities | |
| Lipoic Acid | 23 | Low | Vitamin | May help to protect the body from Arsenic Poisoning | |
| Nerve growth factor NGFR precursor | 23 | Low | Protein | Cell surface receptor, receptor activity, signaling trans. | |
| Neurotensin receptor 2 | 23 | Low | Protein | Cell comm., signal transduction, brain | |
| Pantothenic Acid | 15 | Low | Vitamin B5 | may reduce aggressiveness | |
| Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) | 15 | Low | Toxin | May extend Lifespan | |
| Janus kinase & microtubule interacting protein 1 isoform 1 | 15 | Low | Protein | Reg. of nucleotase, nucleoside, nucleotide, nucleic acid | |
| Folic Acid | 13 | High | Vitamin | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic | |
| Folic Acid | 13 | High | Vitamin | Enhances brains production of energy | |
| Oncomodulin | 13 | High | Protein | Regenerates injured nerve fibers, brain, spine | |
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | 13 | High | Epigenetic | contributes to depression |
| GABA A receptor assoc protein | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Mediates with cytosleleton |
| GABA A receptor alpha 1 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Assoc. w/ epilepsy, juvenile myoclonic |
| Ghrelin | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Growth horm. involved w/ memory, obesity, anorexia |
| Catalase | 64 | 0.00 | High | Enzyme | May possess life extension capabilities |
| Ghrelin | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Growth horm. involved w/ memory, obesity, anorexia |
| GABA A receptor assoc protein | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Mediates with cytosleleton |
| Catalase | 64 | 0.00 | High | Enzyme | May possess life extension capabilities |
| HTR 5- hydroxytryptamine receptor 2c | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Serotonin receptor |
| GABA A receptor alpha 1 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ epilepsy, juvenile myoclonic |
| Cholinergic receptor muscarinic 2 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Influences many effects of CNS E peripheral NS |
| Cholinergic receptor muscarinic 2 | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Influences many effects of CNS E peripheral NS |
| Acetylcholine CHMR 5 (muscarine) | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | Involved w/ personality traits |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ clotting, stroke |
| Fibrinogen alpha gene | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | controls blood clotting assoc. w/ stress |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Protein metabolism, protein binding |
| Fibrinogen, alpha chain | 64 | 0.00 | High | Genome | Assoc. w/ clotting, stroke |
| Fibrinogen alpha gene | 64 | 0.00 | High | Protein | controls blood clotting assoc. w/ stress |
| Acetylcholine CHRNA5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Cell comm., signal trans., dev. of nervous system |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic alpha polypeptide 5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Assoc. w/ brain, nervous system dev. |
| Nitric Oxide | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Biochemical | May possess life extension capabilities |
| Cystine | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 28 | 0.04 | Low | Protein | Assoc. w/ ADHD, brain, nervous system |
| Dopamine receptor D5 | 20 | 0.04 | High | Protein | Assoc. w/ ADHD, brain, nervous system |
| Cystine | 20 | 0.04 | High | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic |
| GABA receptor alpha 5 | 20 | 0.04 | High | Epigenetic | Autism, Praeder Will/Angelman syndrome, bipolar |
| GTP Atlastin | 24 | Low | Epigenetic | ER/Golgi activity, cell comm., signal transduction | |
| Atlastin | 24 | Low | Epigenetic | ER/ golgi activity, spastic paraplegia, brain | |
| Acetylcholine CHRNA 10 (Nicotinic agonist) | 24 | Low | Genome | Transport chain, int. ear, hair cells, skin cells keratinocytes | |
| Cholinergic receptor neuronal nicotinic alpha polypeptide 10 | 24 | Low | Genome | Internal ear, hair cells, pituitary gland, keratinocyte |
| Solute carrier family 6 member 3 | 24 | Low | Genome | Brain & retina, protect against nicotine dependence | |
| GABA A receptor assoc protein | 16 | High | Protein | Mediates with cytosleleton | ||
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | May facilitate the excretion of Arsenic | ||
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | Autistics may be deficient in | ||
| Taurine | 16 | High | Amino Acid | Concentrates in brain | ||
| NGFR associated protein 1 | 21 | Low | Genome | Oligodendrocytes myelinating cells of CNS | ||
| Nerve growth factor NGFR AP 1 | 21 | Low | Genome | Signal transduction, apoptosis | ||
| the issue | ||||||
References:
http://www.cnn.com/2017/10/13/politics/cuba–us–diplomats–acoustic–weapons/index.html
https://www.dicardiology.com/content/research–shows–correlation–between–coronary–artery–disease–and–voice
https://www.theverge.com/2017/9/16/16316048/sonic–weapon–cuba–us–canadian–diplomats–ultrasound–infrasound–science
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2017/10/12/sound–us–diplomats–sonic–attack–cuba/
https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2017/09/30/all–the–theories–about–whats–happening–to–the–diplomats–incuba/?utm_term=.c34734fbd6d1
STATEMENT OF FACT: The information herein contains opinions concerning correlations between personality traits and frequencies found within the voice. The computer printouts are generated by a computer using fast Fourier transforms and voice spectral analysis developed by the Institute of BioAcoustic Biology – a non-profit research organization: SoundHealthOptions.com – 740-698-9119.

